As we can see on [2] “The Indexed Web contains at least 2.02 billion pages (Saturday, 05 July, 2014)”.
As a consequence we need to use a service of a web search engine if we want to find something of interest on the Web or answers to some questions .
For this reason search engines are generally used as “Internet users' entry point to the digital world” [1] to make their searches (according to ComScore [3] searches are defined as “user engagement with a search service with the intent to retrieve search results.”).
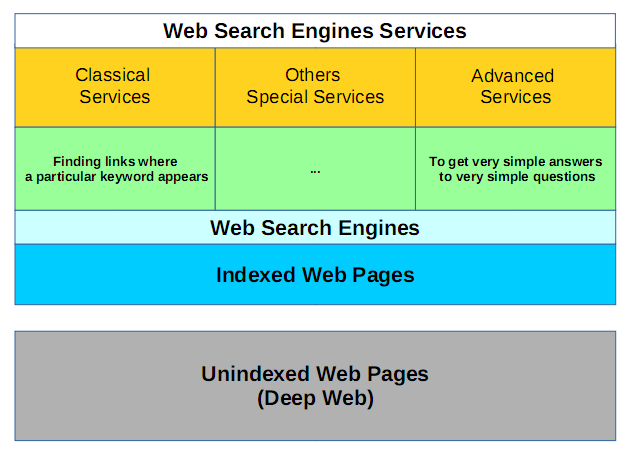
In the following figure we can see an outlook of web search scenario in relation to the huge quantity of web pages.
We have many types of web search engines working on indexed pages:
- GENERAL SEARCH ENGINE like Google, Bing and Yahoo;
- COMPUTATIONAL KNOWLEDGE ENGINE like www.wolframalpha.com;
- ANSWER SEARCH ENGINE like www.chacha.com;
- IMAGE SEARCH ENGINE like www.picsearch.com;
- VIDEO SEARCH ENGINE like on.aol.com;
- TORRENT SEARCH ENGINE like www.ktorrents.com;
- PERSON SEARCH ENGINE like www.spokeo.com;
- EMAIL SEARCH ENGINE like www.emailsherlock.com;
- BUSINESS SEARCH ENGINE like www.business.com;
- BLOG AND FORUM SEARCH ENGINE like omgili.com;
- META-SEARCH ENGINE like www.dogpile.com.
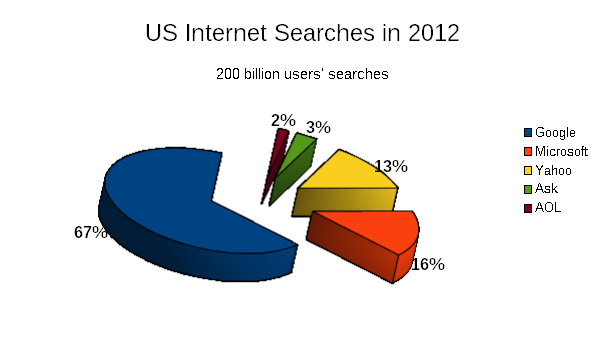
As we have many search services, the web search is still dominated by Google, Microsoft and Yahoo. The following figure gives a clear idea even if it's referred to 2012. The graph in the figure is based on 200 billion searches done in the United States in 2012 [1].
The next step for the web search engines will be the semantic search because people are going to commuicate with them in a way that's much more natural to their thinking. So the web search engines should try to understand the meaning and, in relation to it, should give the more appropriate and pertinent answer.
REFERENCES
- The Global Edition of the New York Times. Friday, April 5, 2013 page 15. “Web Searches that try to read your mind”;
- http://www.worldwidewebsize.com/;
- http://www.comscore.com/: Analytics for a Digital World™.