Continuous improvements of ICT technologies give exponential accelerations to all areas in all private and public sectors.
The gold for a private or public manager/diplomat is to keep up with the changes caused by new technologies by using a soft skill approach.
Diplomats should be efficient and flexible and should possess a high ability to adapt to the fast changes of the world.
In this scenario, we assist to an improvement in the development of open source intelligence (OSINT) tools and techniques.
OSINT is the act of gathering intelligence through exploiting all the information that is publicly available.
Wikipedia defines OSINT as “Open-source intelligence (OSINT) is a multi-factor (qualitative, quantitative) methodology for collecting, analyzing and making decisions about data accessible in publicly available sources to be used in an intelligence context.” [02]
The amount of publicly structured data, semi-structured data e unstructured data is huge. We need skill for analyzing them in order to make correlations, extracting information and then knowledge, which could be used for predictions or making policies and strategies.
Many governmental and non-governmental structures use OSINT services: government organizations, Economist Intelligence Unit, BBC, who do investigative journalism, many private corporations for commercial advantages and do son.
Why not use OSINT services in the diplomatic field? Diplomacy could gain advantages on knowledge obtained by OSINT services putting into operation strategies and policies in a predictive way especially in the economic sector.
OSINT smart prediction machine
The scheme of work of OSNT is simple:
- Gathering and collecting all type of public data you can in any form;
- Organize them in a way you can manipulate;
- Analyze them and find hidden correlations;
- Generate information and statistical projections;
- Produce useful knowledge.
Here it is the machine model:
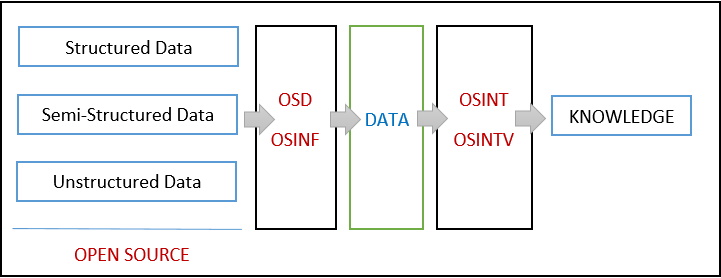
where:
- Open Source Data (OSD): datasets, survey data, metadata, audio or video recordings and so on;
- Open Source Information (OSINF): books on a specific subject, articles, interviews and so on;
- Open Source Intelligence (OSINT): all information discovered, it is the output of open source material processing;
- Validated OSINT (OSINT-V): OSINT confirmed/verified using highly reputable source.
REFERENCES
[01] Clima, energia e digitalizzazione: le sfide per la diplomazia economica 4.0 - Intervista a Marco Alberti a cura di Alessandro Strozzi: Pandora Rivista N.3/2020;
[02] https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Open-source_intelligence Open-source intelligence;
[03] Nihad A. Hassan, Rami Hijazi, Open Source Intelligence Methods and Tools, Apress 2018;
[04] Michael Bazzell, Open Source Intelligence Techniques 5th edition, 2016